
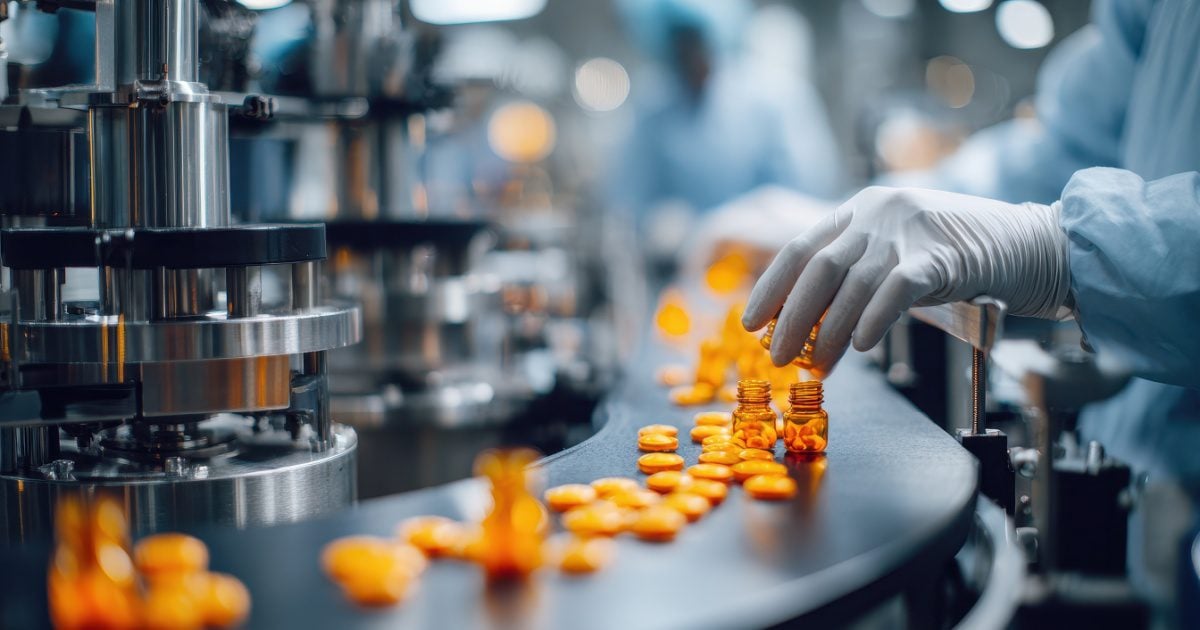
Sweet solutions for the bitter pills in the pharmaceutical supply chain

The pharmaceutical supply chain is a complex global network, a lifeline crucial for delivering life-saving medications to patients around the world.
The race against time for life-saving drugs is real. The pharmaceutical supply chain operates in a high-stakes environment, constantly facing challenges that can disrupt the flow of essential drugs and compromise patient safety.
The lifecycle of a pharmaceutical product
This pipeline begins with pharmaceutical companies developing or sourcing essential ingredients in two forms:
- Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), which help to produce the intended health effect, are manufactured using a range of synthetic and biological raw materials.
- Excipients are any substances other than the API that help deliver the medication into the patient’s system. They are chemically inactive, allow the medicine to remain stable, and control the absorption of the drug.
After development, pharmaceutical manufacturing begins, where drugs are produced, packaged, and labeled according to these categories:
- Raw materials and bulk pharmaceuticals: Chemical compounds and APIs
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) medicines: Vitamins, minerals, supplements, common drugs, and dermatology products
- Prescribed drugs: Opioids, benzodiazepines, and stimulants
- Biologics: Vaccines, blood, allergens, genes, and tissues
From there, a wholesaler purchases the medications directly from the manufacturer, which is then passed to a distributor/storage provider for logistics handling.
Lastly, the drug product gets to the patient at the endpoint of the pharmaceutical supply chain through:
- Hospital or clinic,
- Pharmacy or retail, or
- Mail order
Combating the flood of counterfeit drugs
Unfortunately, fake medicine is a booming business. Counterfeit drugs generate about US$83 billion (€77.2 billion) in global sales annually, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). This is largely concentrated in developing countries, where 1 in 10 medical products sold is counterfeit.
In 2023, Danish pharmaceutical company Novo Nordisk reported a significant increase in counterfeit sales of its popular weight-loss and diabetes drugs, Wegovy and Ozempic, on online platforms. These illicit versions most likely contained incorrect dosages, harmful ingredients, or no active pharmaceutical ingredients, putting users at serious risk.
Counterfeit drugs run rampant due to a lack of fast and accurate end-to-end visibility throughout the complex pharmaceutical supply chain.
Thus, the use of Track-and-trace technology, such as computer vision, can quickly scan the unique barcodes or QR codes of each pharmaceutical product, thereby solving this conundrum. This "digital passport" allows stakeholders to receive real-time alerts about missing or unreadable barcode labels. The subsequent quick action to rectify these issues can prevent counterfeit medications from entering or remaining in the legitimate supply chain.
A smart approach to keeping it cool
Another key challenge in the pharmaceutical supply chain is maintaining precise temperature ranges for pharmaceutical products like vaccines and biologics.
The pharmaceutical product must remain within a specific temperature range throughout the entire journey, ranging from 2-8°C to ultra-cold temperatures down to -196°C.
According to WHO, failures in temperature-controlled cold chain logistics cost the pharmaceutical industry about US$35 billion (€30.2 billion) annually. Nearly 50 percent of vaccines are wasted annually due to improper temperature management.
The cold chain delivery process is particularly challenging in remote areas. Poor road infrastructure and intermittent electricity supply present significant last-mile challenges during the final leg of delivery.
To tackle these issues, devices powered by the Internet of Things (IoT) can be deployed for cold chain monitoring. These smart sensors provide real-time data on temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors. The continuous temperature monitoring, near real-time data analytics allows for an equally quick action to protect the integrity of the medicines throughout the entire journey.
Governments and welfare organizations are crucial players in expanding the reach of cold chain solutions, particularly in remote and/or developing areas. Investments in infrastructure and distribution methods can ensure the integrity of essential drugs and vaccines.
The work of Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance exemplifies the importance of collaboration and innovative solutions. In 2021, Gavi, UNICEF, and the Congolese government jointly opened a massive 12,000m3 cold chain warehouse for the storage of Covid-19 and other vaccines in Kisangani city. This hub is supported by canoes and boats for nationwide distribution, greatly reducing the reliance on costly air transport for vaccine delivery.
Gavi also launched the Cold Chain Equipment Optimization Platform (CCEOP), which delivered over 5,800 solar-powered fridges to rural clinics in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), combating inconsistent electricity and reducing vaccine spoilage.
Delivering the cure for the e-prescription boom
On the digital front, the global online pharmaceutical industry is projected to have a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.6 percent from 2025 to 2029, resulting in a potential market volume of US$130.5 billion (€121.3 billion) by 2029.
An increasing number of patients have turned to virtual clinic visits, leading to a surge in e-prescriptions being issued. The challenges from delivering prescriptions to patients’ doorstep is combined with the rise in individuals who require consistent medicine refills for chronic conditions.
As online health consultations become mainstream, the pharmaceutical industry must focus on micro-fulfillment operations to maintain supply chain integrity. Local pharmacies like Walgreens have micro-fulfillment centers that use robots to fill prescriptions for roughly 60 percent of orders, streamlining routine tasks and reducing excess inventory from the pharmacy.
Protecting the pharmaceutical pipeline from geopolitical instabilities
The pharmaceutical supply chain operates like a vast global village in today's interconnected world. Raw materials might originate in one continent, undergo manufacturing in another, and then be distributed across the globe.
Geopolitical issues, ranging from tariffs on goods to international conflicts, can disrupt global supply routes, impact raw material availability and create trade barriers.
Global disease outbreaks can also cause rapid demand swings for certain medications, such as ventilator sedatives, personal protective equipment (PPE), as well as vaccines and antiviral treatments.
Manufacturers may consider creating safety stock, which is calculated as:
(Maximum amount of sales x Maximum lead time) – (Average amount of sales x Average lead time).
Safety stock acts as a buffer against unexpected demand surges or supply disruptions, ensuring continuous product availability.
The formulas to calculate safety stock, and determine the health level of your inventory, are:
- Standard deviation safety stock: Z × σLT × D avg, which uses the standard deviation of demand during lead time to account for variability.
- Safety stock with a variable lead time: Z x Average sales x σLT, which specifically addresses situations where the lead time itself is inconsistent, using its standard deviation.
- Economic order quantity: √(2DS/H), which determines the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, not directly safety stock, but related to ordering strategy.
- Reorder point: (Average stock depletion in the given period x Average lead time) + Available safety stock, which calculates the inventory level at which a new order should be placed to avoid stockouts, incorporating safety stock.
- Inventory position: Inventory on hand – Backorders + Inventory currently on order, which provides a real-time view of the current inventory available and expected, considering outstanding orders and unfulfilled demand.
From lab to patients: Bridging the gaps in pharmaceutical logistics
When a patient's health hangs in the balance, every link in the pharmaceutical network counts. A robust supply chain ensures life-saving medicines reach every patient worldwide.
While the ecosystem battles many ailments from counterfeit medicines to geopolitical instabilities, collaboration with key stakeholders and investments in technological advancement are powerful cures to these challenges.
ALSO WORTH READING














 English
English