
Next-gen wireless: Why LPWAN is essential to the future of IoT in logistics
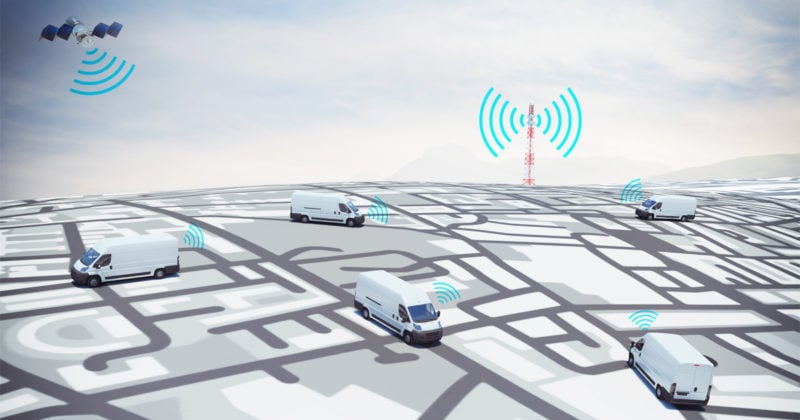

A small sensor attached to a delivery truck blinks steadily, pinging signals at fixed intervals to a central dashboard tracking shipment visibility.
Back in the warehouse, hundreds of roll cages, with sensors attached, cruise around swiftly for dispatch as the operations team watches on from a similar dashboard.
Powering these sensors is a simple yet cost-effective technology — known as Low-Power Wide-Area Network (LPWAN) — which could shape the future of Internet of Things (IoT) across industries including logistics.
The hype around 5G has grown significantly in recent years, with many dubbing the fifth generation of cellular internet connectivity a potential game-changer for IoT applications. But the rollout of 5G has encountered roadblocks in different countries such as high costs, lack of compatible devices, and insufficient network coverage to support the new technology.
As the real impact of 5G’s exponentially faster data speeds and reduced latency is yet to be seen, LPWAN technologies have quietly forged ahead as a low-cost, fuss-free alternative.
So what exactly is LPWAN and why is it essential for the logistics industry?
LPWAN, explained
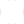
In short, LPWAN technologies are inexpensive, consume little power, and are highly reliable, according to the ‘Next-Generation Wireless in Logistics’ report by DHL Trend Research.
The data transmitted from LPWAN devices is minimal as compared to everyday devices such as computers or smartphones. Depending on the frequency and the quantity of data transmitted, LPWAN devices tend to operate with reasonable battery life and can run on lower-cost batteries because of its relatively low peak power requirements.
In the next-generation wireless ecosystem, LPWAN technologies are designed to fill a void by offering the functionality of short-range technologies like Bluetooth and Radio-frequency Identification (RFID), but transmitting over distances equivalent to the costlier 4G and 5G mobile technologies.
Unlike 5G, LPWAN technologies are widely used today, allowing customers to tap on existing infrastructure.
Examples include Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) which maximizes coverage using existing base station infrastructure, and LTE-M, a simplified version of the LTE technology that supports 4G mobile networks. LTE-M provides slightly higher data rates and lower latency than NB-IoT, but requires more power to operate.
The barriers of entry to set up an LPWAN infrastructure are much lower as compared to that of setting up a conventional cellular network. It costs significantly lesser given the cost-effectiveness and range of a single base station, which allows more devices to be connected across a wider area.
This has led to the emergence of two prominent independent LPWAN technologies, both of which use unlicensed frequencies.
One of them is Sigfox, a narrowband technology suitable for sending small, infrequent bursts of data. The other is LoRa (short for long range), an open standard for LPWAN technology that ensures good receiver sensitivity and low bit error rate (BER) from inexpensive chips — or basically, an extended range compared to other radio technologies.
What this means for logistics
Best used where data transmission is low and where lag time does not compromise operations, LPWAN technologies have the potential to be applied in different industries. Possible uses can include remote monitoring of access control systems in carparks or hotels, or as a tracking technology.
“The affordability and functionality of LPWAN technologies make it an ideal fit for new use cases in the logistics industry where asset tracking is crucial in ensuring end-to-end visibility and building a resilient supply chain,” explained Christopher Fuss, Head of DHL SmartSensor and IoT Solutions, DHL Customer Solutions & Innovation.
In China, DHL Supply Chain partnered with Chinese telecommunications giant Huawei to test an NB-IoT system designed to improve yard management at a major automotive logistics site.
In-ground sensors at warehouse dock doors, parking spaces and staging lots, feed operational data to a central yard management dashboard. This helped to orchestrate the movement of around 100 DHL drivers and vehicles as they managed the inbound handling of parts headed for car production lines.
In another example, a French aeronautics company integrated 14,000 tracking sensors into its manufacturing containers to monitor items in transit within its extensive facilities. These sensors include LED light indicators that blink when staff members search for a specific crate or work order. The use of sensors has since reduced product lead time and downtime in its operations.
Besides offering such levels of visibility that can prevent any potential loss of assets, LPWAN also generates cost savings by enabling predictive maintenance and reducing energy consumption, while still ensuring operational efficiency.
With more industries emphasizing on supply chain visibility and tracking, new and existing LPWAN technologies look set to dominate with its simple, cost-effective devices in an IoT future.
To find out more on the potential of next-gen wireless technologies, read the latest DHL trend report here:
ALSO WORTH READING











 English
English