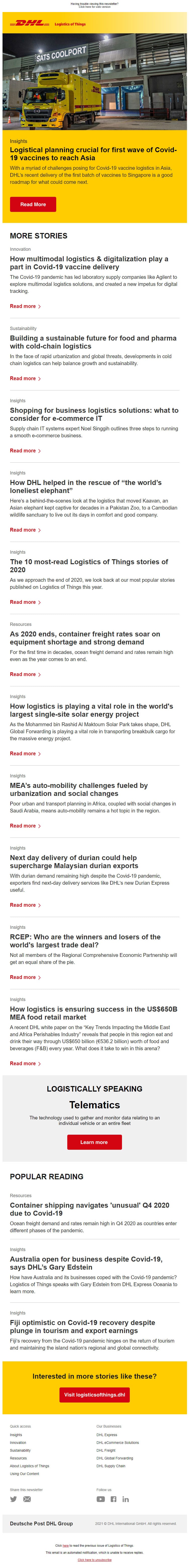
Offsetting

Offsetting carbon emissions is the process of compensating for carbon emissions produced through human activities such as transportation, manufacturing, and energy production.
Carbon offsets are being put forward by shippers, carriers and logistics service providers to compensate for emissions they cannot mitigate within their operations or supply chains. By offsetting their carbon emissions, individuals, businesses, and organizations can achieve carbon neutrality, balancing their carbon emissions with an equal amount of carbon reduction or removal.
Companies conduct offsetting activities by investing in projects that reduce or remove greenhouse gas emissions from the atmosphere. This is typically done by purchasing carbon credits, which represent a certain amount of carbon that has been reduced or removed from the atmosphere through projects such as renewable energy production, reforestation, or methane capture.
However, third-party organizations must verify and certify carbon offset projects to ensure they meet established carbon reduction or removal standards. For example, DHL’s GoGreen climate-neutral service helps businesses invest in internationally recognized climate protection projects that generate at least the Verified Emission Reductions (VER) Gold Standard credits. The logistics leader has also invested in its very own independent project in Lesotho, which has been certified under the new Fairtrade Climate Standard since 2016.
Overall, while it is not a substitute for reducing carbon emissions at the source, carbon offsetting is important for mitigating the effects of human activity on the environment and contributing to a more sustainable future.





 English
English