Exoskeletons
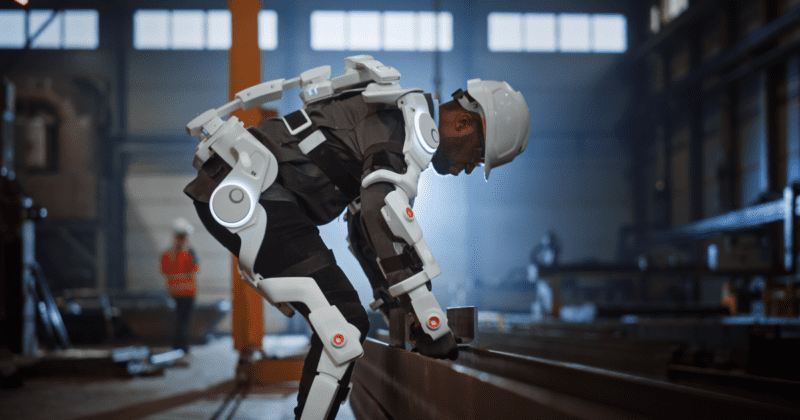

Musculoskeletal diseases are one of the most common work-related health issues, affecting over 1.7 billion individuals globally. Aiming to reduce such ailments, the exoskeleton – a device worn on the outside of a person's body designed to augment or enhance the wearer's natural abilities – was invented to provide additional strength, endurance, and mobility to workers performing physical labor.
Exoskeletons originated from healthcare and military industries, primarily used for medical rehabilitation and injury prevention. Active and passive devices that support different parts of the body have advanced in usability, form factor, and performance in the past two years.
In 2021, the exoskeleton market was estimated at USD 257.9 million and is expected to have a compound annual growth rate of 18 percent from 2022 to 2030 – indicating wider adoption in workplaces. Today, exoskeletons are deployed for various commercial uses and even developed for space exploration.
While exoskeletons are projected to have minimal effect on supply chain operations, the technology is beneficial to employee health and safety. With an aging workforce and increasing labor shortages, the logistics industry is keen to see how exoskeletons, capable of reducing physical strain, could protect employees from potential work injuries.
Logistics providers such as DHL plan to adopt exoskeletons as a more prevalent solution in their warehouses, from lower back support exoskeletons for heavy lifting to chair-like reinforcement for standing workers.





 English
English