Digital Bunkering
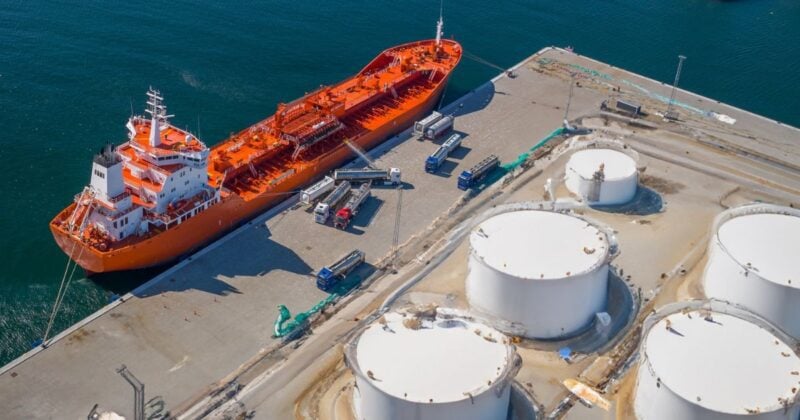

Bunkering is the process of supplying fuel to ships. It involves several steps, such as delivering and transferring fuel from storage tanks to ships and ensuring that the fuel meets quality and regulatory standards. Today, digital bunkering is gradually replacing traditional processes throughout the bunkering value chain. Its technology offers numerous benefits in administration, fuel monitoring, delivery schedules, etc.
By digitizing documentation, digital bunkering reduces the need for physical paperwork — such as bunker delivery notes (BDNs) — by replacing them with electronic bunker delivery notes (eBDNs). Using e-BDNs streamlines workflows and takes inventory of the fuel’s details like its origin, quality and amount. Compared to paper-based BDNs, the electronic process increases efficiency whilst offering stakeholders easy access to information.
Digital bunkering platforms utilize mass flow meters (MFMs) which measure the quantity of fuel transferred during bunkering. Integrating MFMs with real-time information on fuel availability at various ports ensures that vessels can secure the necessary fuel without delays. This system also ensures that the specifics of fuel, such as type and quantity, are accurately documented to meet environmental regulations like MARPOL Annex VI — which sets limits on sulfur emissions from ships. Tracking emissions in real-time can provide data for reporting and present alternative fuels as more sustainable options.
Digital bunkering automates fuel delivery scheduling, optimizes logistics, and reduces waiting times at ports. This is particularly beneficial in busy ports where delays can be costly. By analyzing historical data and current conditions, these systems can predict potential fuel delivery delays, allowing operators to adjust their schedules accordingly. In addition, it offers dynamic pricing based on live market conditions, helping ship operators make informed purchasing decisions.




 English
English