Cost, Insurance and Freight (CIF)
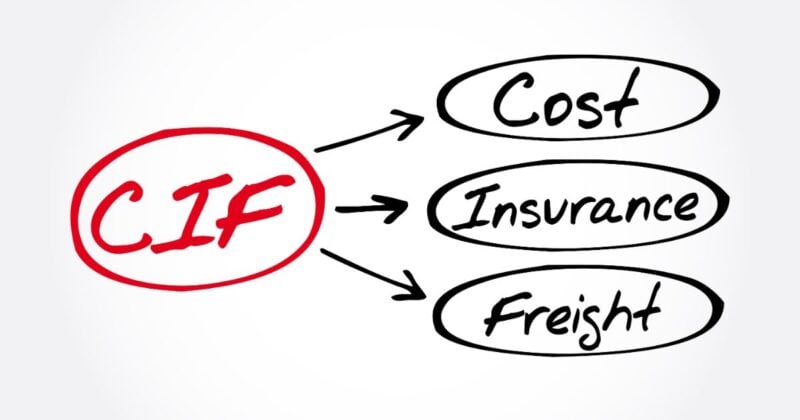
CIF is an important shipping term that applies to both the seller and the buyer in an international trade transaction. The seller is responsible for the costs associated with transporting goods to a designated port, ensuring a smoother transaction for both parties involved. It is primarily used for ocean or inland waterway transport.
Key components of CIF include:
Cost: Refers to the total cost of goods being sold. This includes the base price of the products and any additional expenses such as transportation costs, export duties, and taxes.
Insurance: The seller must purchase minimum insurance coverage to protect the goods against damage or loss during transit. This insurance typically covers at least 110 percent of the commercial value of the goods, protecting both parties from potential losses. The buyer is named as the beneficiary of this insurance.
Freight: Refers to the transportation costs incurred by moving goods from the seller’s location to the destination port. The seller must arrange and pay for the freight charges, which can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and the nature of the goods being shipped.
Once the goods arrive at the destination port, the buyer is responsible. At this point, the buyer is responsible for all costs related to unloading the goods at the destination port, inclusive of customs clearance, transportation, and any applicable duties or taxes.
CIF is commonly used for bulk commodities and goods shipped in large quantities, such as oil, coal, and grain. It provides clarity on the division of responsibilities and liabilities in international trade, helping to manage risks and costs effectively.





 English
English