Centralized Examination Station (CES)
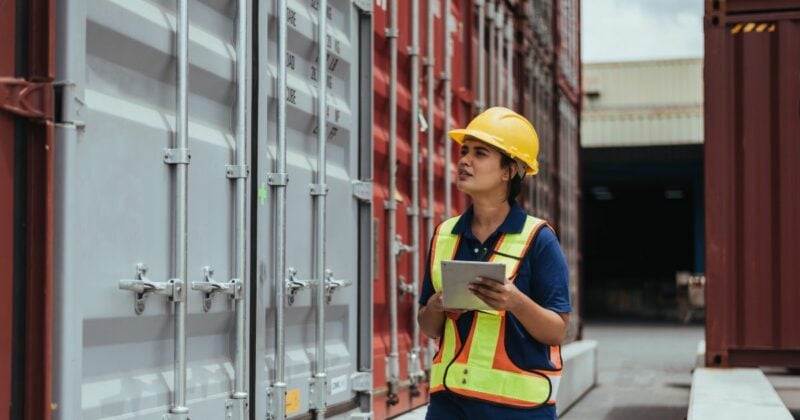

Centralized Examination Stations (CES) are opened by the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) to address challenges posed by the increasing volume of containerized shipments arriving at ports. These facilities aim to centralize and streamline the examination process for imported cargo into the U.S.
The CES process begins with notification and confirmation of a container's availability. Upon arrival, the container undergoes exams specified by CBP instructions. Cargo may be held for further inspection, with release status trackable via the CES system, before being released and delivered.
CES boosts inspection efficiency by consolidating multiple examination activities into a specialized facility. Some of the common CES exams include Backdoor, Vehicle And Cargo Inspection System (VACIS), Contraband Enforcement Team (CET) examination, and a United States Department of Agriculture examination (USDA), All stations are equipped with advanced technologies to systematically and comprehensively examine if the goods comply with customs compliance.
The strategic placement of CES also plays a role in boosting efficiency. These facilities are located near major ports to reduce the time and resources required for examinations. Most cargo going through CES is released within 24 hours of their arrival.
With the success of CES dedicated to ocean freight, the CBP has also opened the first Air Centralized Examination Station (A-CES) at Los Angeles International Airport (LAX) in 2021. This was a response to the massive growth in e-commerce shipments from 2019-2021 (657 percent). The station is expected to process over 15,000 shipments every day.




 English
English