Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)

What are Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)?
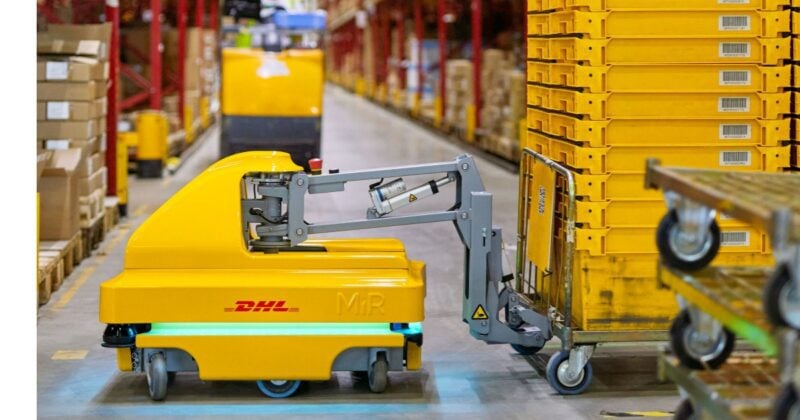
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are indoor mobile robots designed to move and complete tasks inside facilities without direct human control. They differ from earlier automated guided vehicles (AGVs), which follow fixed physical or digital paths. AMRs instead use real‑time path planning, allowing them to move freely, avoid obstacles and adapt to fast‑changing warehouse environments.
How are AMRs evolving in logistics?
AMR technology has advanced from simple 2D lidar autonomy to more capable 3D visual autonomy, improving accuracy, awareness and performance. This shift has accelerated adoption across warehouses, helped by rapid innovation in sensors, robotics components and software. The entire logistics robotics market is growing quickly, rising from just over US$7 billion in 2022 to more than US$21 billion expected by 2029.
How does DHL use AMRs today?
DHL uses AMRs across its global warehouse network to take over “3D” tasks — dull, dirty and dangerous work that often strains human workers. These robots move along aisles, transport heavy loads, support picking, assist with cleaning tasks and even help with routine safety checks. DHL’s fleet includes solutions such as Locus robots, EffiBot, Avidbots Neo and more, all working alongside people to increase productivity without adding infrastructure complexity.
AMRs also help DHL reduce walking distances in large facilities and raise pick‑rate performance. Globally, DHL has already deployed thousands of AMRs and continues to scale up to meet growing e‑commerce and fulfillment demands.
Why do AMRs matter to warehouse operations?
AMRs improve efficiency by reducing manual movement and enabling faster picking. They also lighten physical strain on workers and free them to focus on problem‑solving or customer‑focused tasks. In high‑labor‑cost markets, they help accelerate order fulfillment and provide real‑time inventory insights to support accurate delivery‑time estimates.
What challenges come with adopting AMRs?
Cost remains the biggest barrier to widespread deployment. Early‑stage AMR technologies such as case‑handling robots show promise but remain expensive. Integrating AMRs with people and processes also requires thoughtful planning. However, once deployed at scale, AMRs can significantly improve operational resilience and create more efficient use of warehouse space.
Why are AMRs important?
By 2030, DHL expects nearly a third of its global material‑handling equipment to use robotic automation. As mobile robots become more affordable and capable, they will continue to shape how warehouses operate — making this one of the most impactful trends in modern logistics.




 English
English