Asset tracking
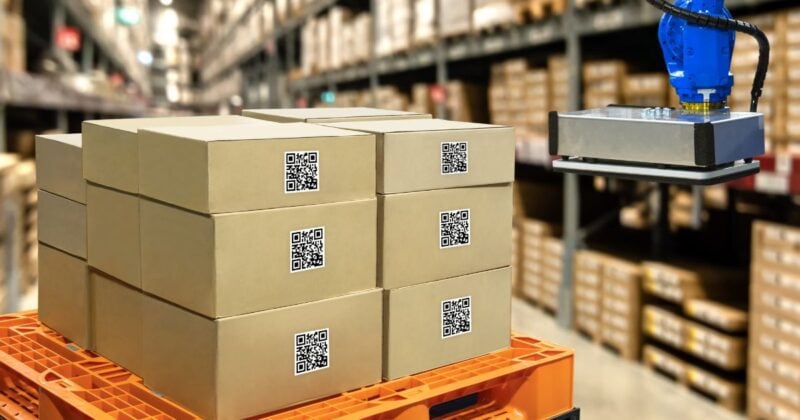

Asset tracking is the systematic process of monitoring and managing an organization’s physical assets throughout their lifecycle. It employs various technologies such as barcodes, Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID), Global Positioning System (GPS), Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and in recent years, the Internet of Things (IOT), to gather real-time data on an asset’s location.
They come in the form of physical tags and are primarily designed for tangible assets, such as machinery and equipment. Documenting the movement and condition of assets makes it easier to comply with industry regulations and prepare for audits or inspections.
For instance, consider each piece of equipment equipped with an RFID tag that broadcasts its location. The site staff can quickly scan the RFID tag with a handheld device to record its exact location on the job site in an inventory system. Workers who need a specific tool or machine can reference the inventory system to locate and collect it.
These tags can also contain information such as the date of purchase and serial number. Such information helps a business track its stock level to make informed decisions regarding asset purchases and allocation. RFID tags can include the products’ date of maintenance to manage their maintenance schedules. A proper asset tracking system can streamline operations, reducing downtimes and increasing efficiency.
In contrast, intangible assets like software licenses do not rely on these traditional methods. They require specialized software to monitor their usage. Automated systems are often employed to facilitate these processes and eliminate the need for physical asset tags.





 English
English