3D Printing
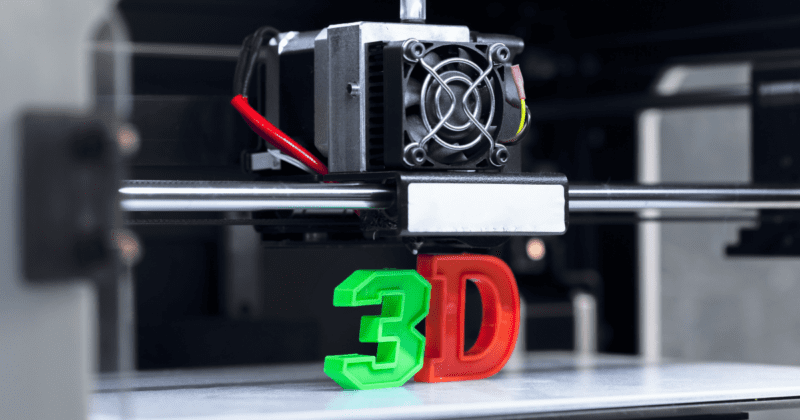
3D printing – also known as Additive Manufacturing (AM) – is a manufacturing process in which a printer builds up successive layers of material to create a three-dimensional object. The technique converts a computer-aided design (CAD) file into a format that the printer can understand and follow the instructions to print the object layer by layer.
First used to speed up the product design process by quickly creating prototypes, the latest advancements in 3D printing have produced lighter, more complex pieces, and in higher quantities. Users also have more options in the materials used – such as plastics, metals, ceramics, and paper – which determine the final product’s weight, strength, durability, accuracy, finish, and other characteristics.
3D printing is now used to create products ranging from simple household items like toys and climbing shoes to complex engineering parts such as semiconductor chips, wind turbines, or medical implants. For example, fuel nozzles for aircraft engines have been 3D printed by GE Aviation since 2015, and have been found to be 25 percent lighter and five times more durable than their conventional counterparts.
Apart from enabling mass customization of end-user parts and products, 3D printing allows companies to store digital part files on the cloud and print products on demand. This gives them the flexibility to optimize inventory and warehouse storage space and achieve shorter lead times.
3D printing can revolutionize local supply chains if they are strong and agile enough to accommodate the efficient distribution of on-demand 3D-printed products. For example, logistics providers could work with 3D printing services to manufacture spare parts in-house, while utilizing their supply chain networks to deliver products efficiently.




 English
English